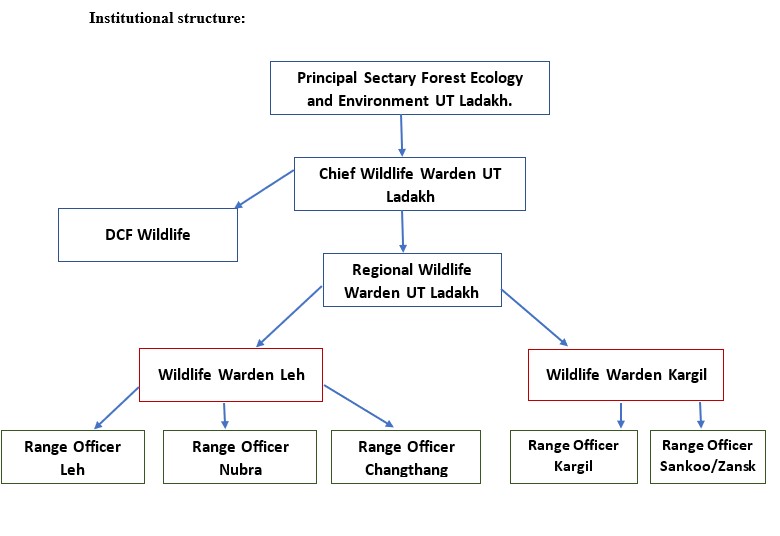
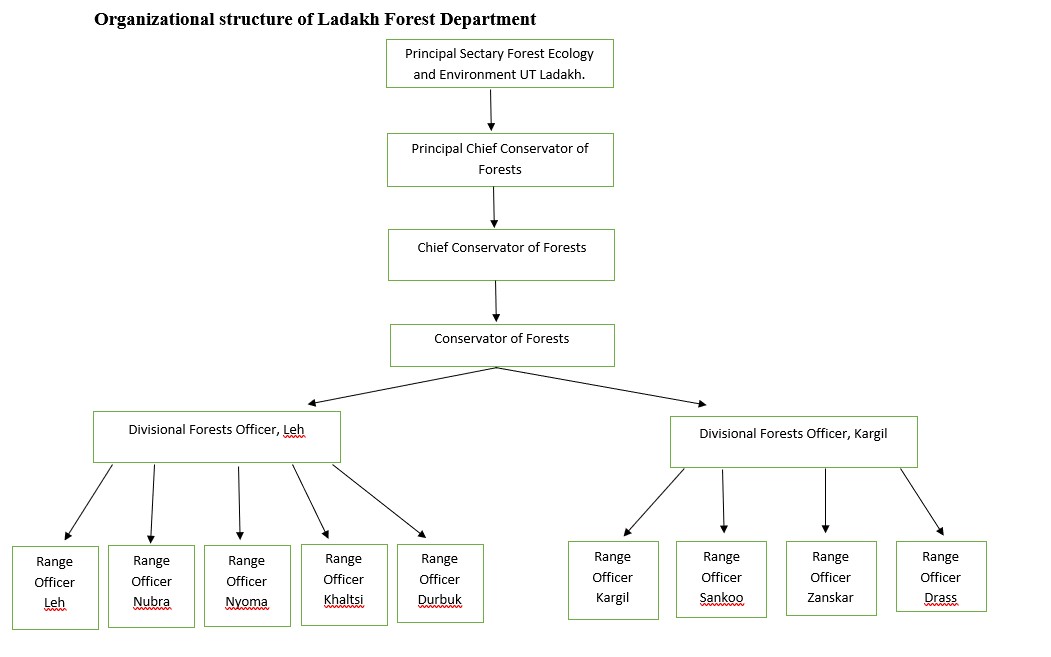
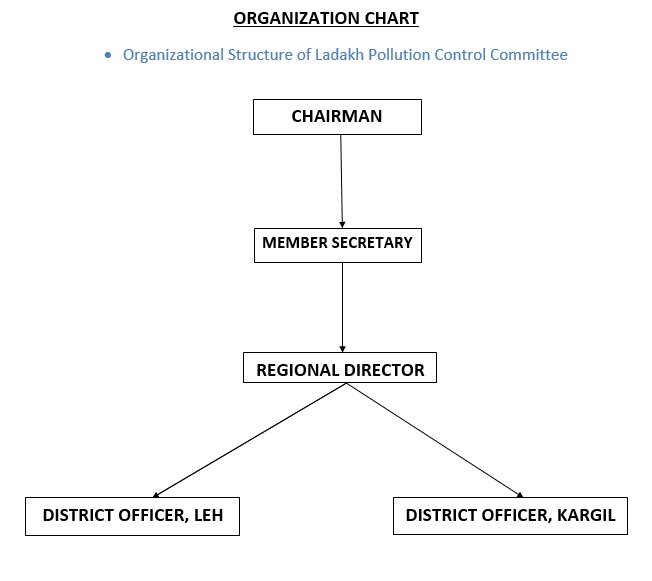
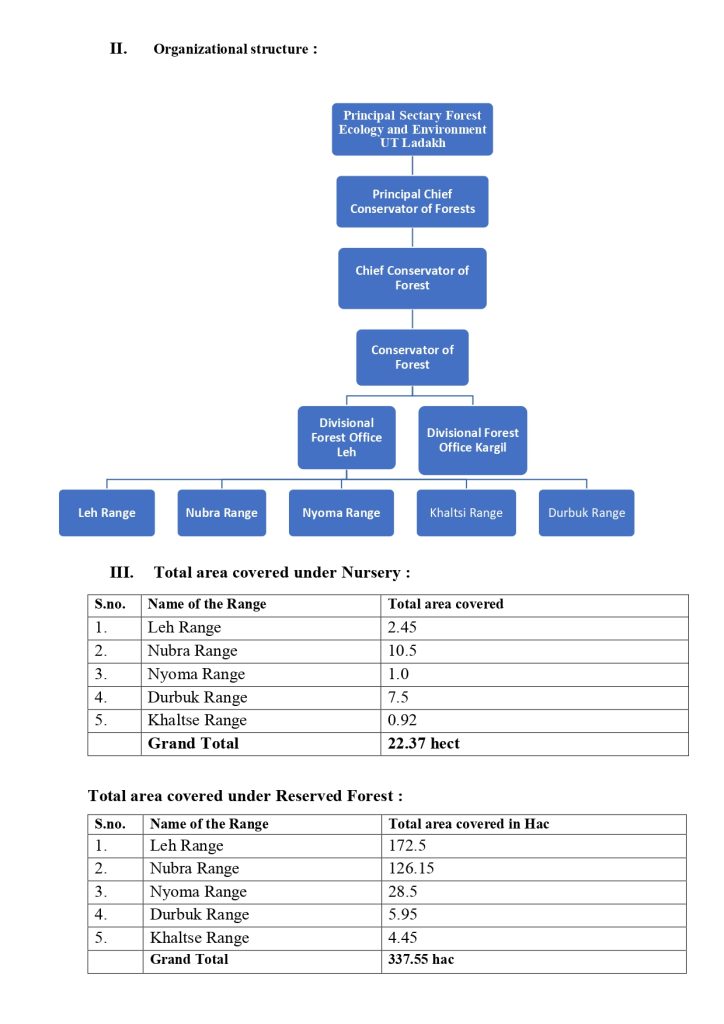
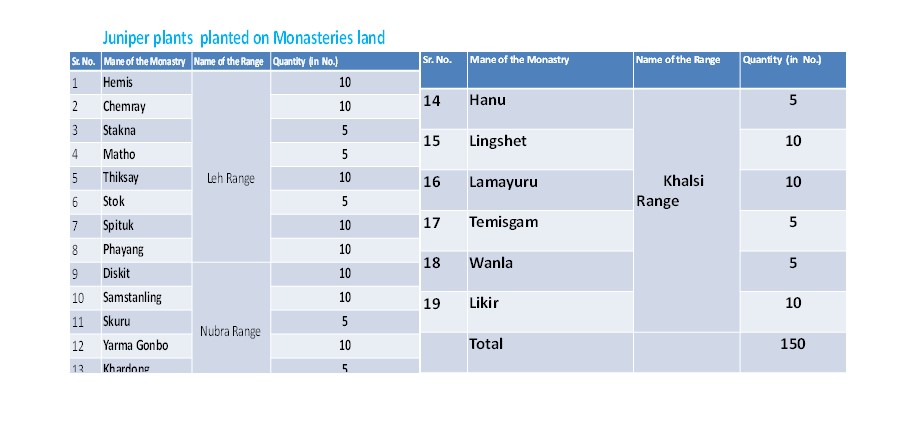
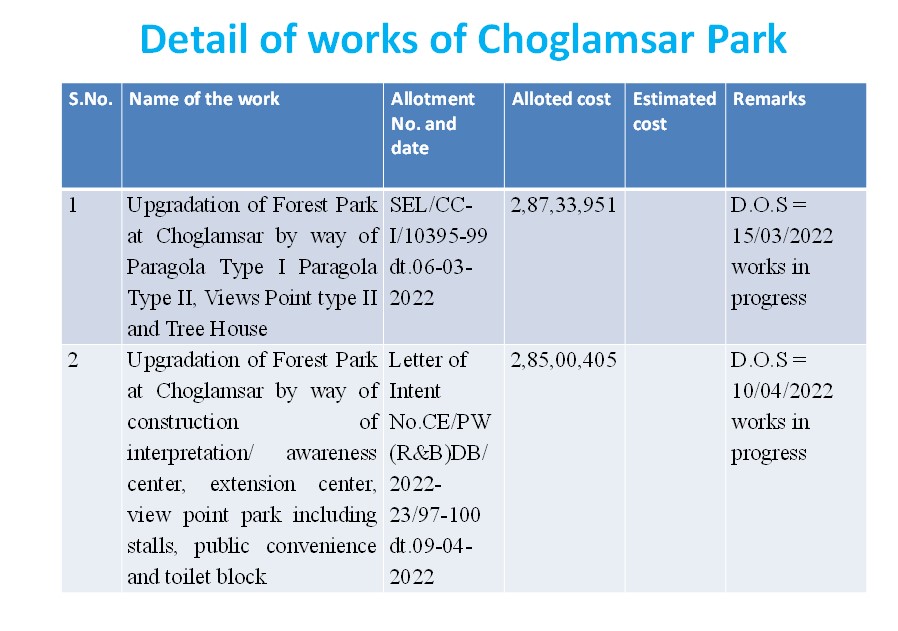
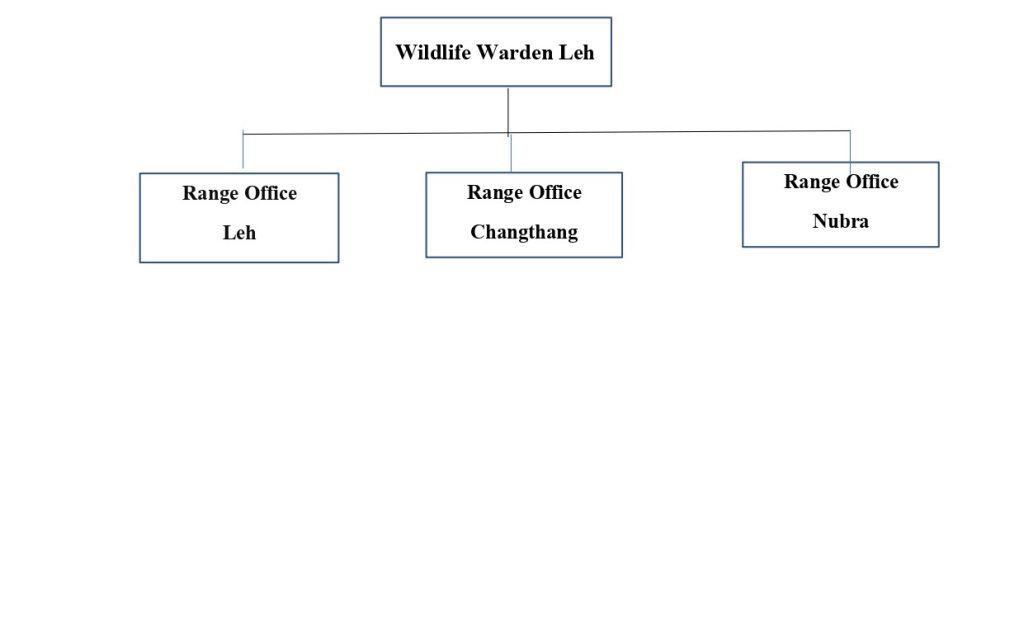
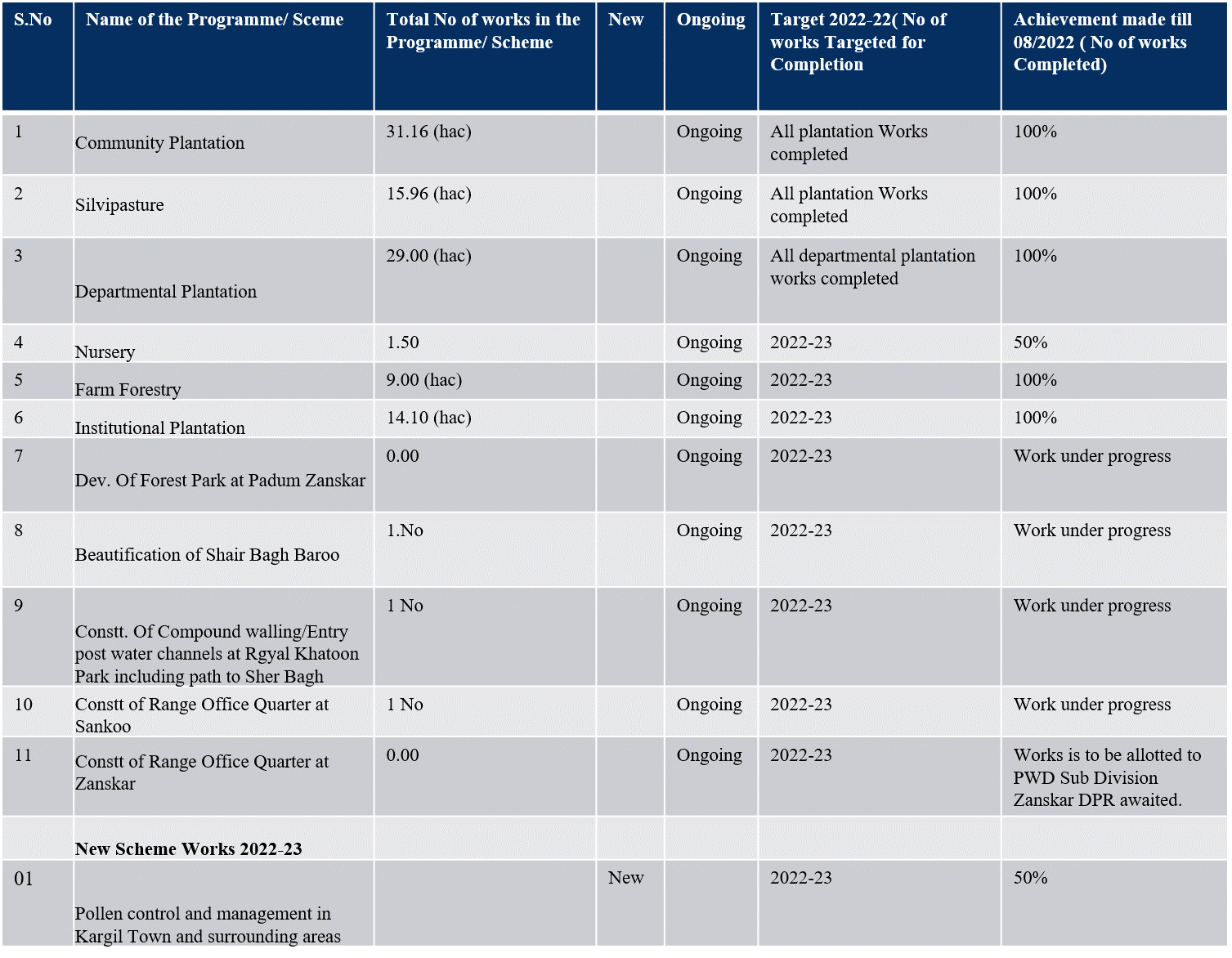
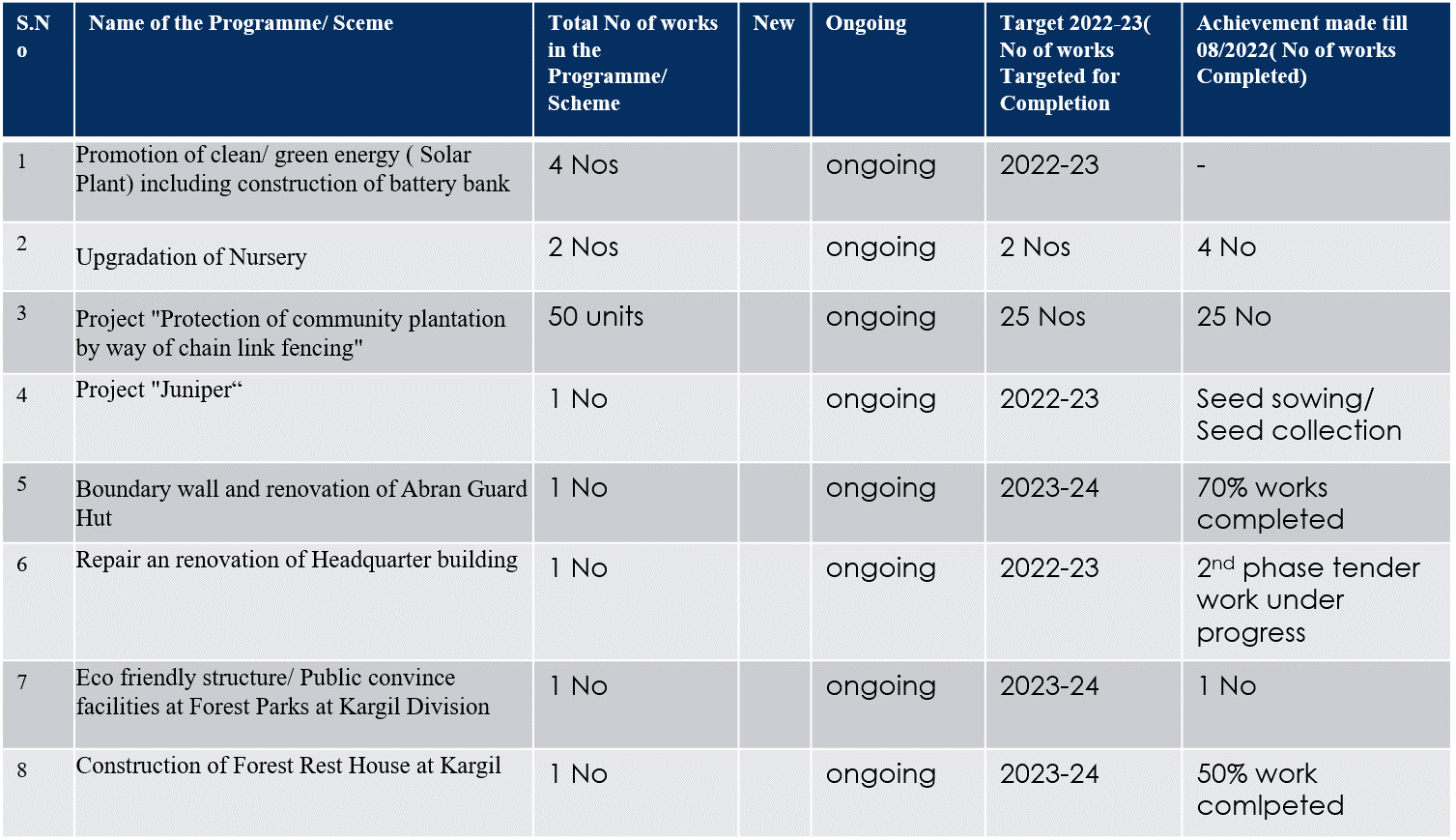
General over view of department
The Department of Wildlife Protection, UT Ladakh, came into existence in the year 1979 (Govt Order NO 132-FST of 1979, dated 13-08-1979) to implement the Jammu and Kashmir Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1978.
The Department of Wildlife Protection, UT Ladakh evolved from J&K Forest Department Game Preservation wing. Since the creation of the Department of Wildlife Protection in 1979, the t department of wildlife protection has taken a series of measures for conservation of forests and the Wildlife therein.
Besides these protected areas two Ramsar sites are also part of the conservation areas under wildlife department Ladakh. Various management activities undertaken in these areas include habitat improvement, plantation, soil and water conservation, anti-poaching activities, development of infrastructure for front line staff, providing supplemental feed to rescued and captive wild animals etc.
Over a period of time, Wildlife Department has focused on management and conservation of wildlife and its habitat on modern lines in consonance with prevalent legislations. After the formation of UT, the Jammu & Kashmir Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1978 was repealed and the Central Act, i.e; Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 became applicable to the Union Territory of Ladakh.
With increasing responsibilities of the department such as wildlife conservation, man animal conflict mitigation, research and education, checking illegal trade in wildlife products and poaching and management of the protected areas, role of the department have multiplied considerably over a period of time. The Department of Wildlife Protection Ladakh is making efforts to come at par with national and international scientific standards as per the recommendations of National Board of Wildlife for management and protection of wildlife.
Aim
Implementation of Wildlife Protection act 1972 and rules made thereunder for achieving the objective of WPA 1972 i.e. to protect the remaining population of endangered species by banning hunting, giving legal protection to their habitats and finally, restricting wildlife trade.
Objectives
- To ensure the long-term conservation of wild flora and fauna of Ladakh through implementation of legal and management provisions of the WPA 1972.
- To encourage public participation and support for the same through providing alternative livelihood opportunities such as development of eco-tourism, trainings and capacity building, to ameliorate the restrictions laid due to implementation of the WPA act.
- To provide the support such as construction of predator proof corals, supply of chain-link fencing, supply of solar appliances for mitigating negative aspects of man animal interaction and for habitat protection.
Major activities of department
- To conserve and protect the bio-diversity of Ladakh.
- To create awareness among the community about the importance of bio-diversity and garner their support for its protection.
- To improve wildlife habitat through physical and biological means.
- To document the Population and distribution of flora and fauna of the Ladakh and undertake various research projects to provide inputs for scientific management of landscape.
- To mitigate human-wildlife negative interactions in the landscape by providing coral pens, chain link fencing, installing Aniders fox light and by organizing awareness camp. Department also provides compensation for livestock depredation by wild carnivores and house and property damage by brown bears.
- To develop institutional monitoring frame work for wildlife crime control and protection of local bio-diversity.
- To support local communities by providing alternative livelihood opportunities through initiatives like promotion of eco-tourism, training and capacity building programs.
- To reduce dependence upon scarce natural resources department is providing various materials such as, furnishing of items for homestays, solar appliance like solar water heater, solar street lights, solar cookers, green houses, dustbins for waste collections, constructions and maintains of local ponds for water retention, etc.